top of page
Patient Presentation: A 23-year-old obese female was diagnosed with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) and referred to neurosurgery for ventriculoperitoneal shunt. A baseline ocular examination was performed prior to the procedure.
On examination, vision was 20/200 in the right eye, and 20/40 in the left eye. There was a right relative afferent pupillary defect. Slit lamp examination was normal.
A dilated fundus examination was performed demonstrating the following:
Retina
Case 1
Patient Presentation: A 67-year-old male presents to an emergency eye clinic with decreased unilateral vision loss from 20/50 to 20/100 OD since last visit. He had cataract surgery one month prior in this right eye. His most recent HbA1C was 5.4%. The patient's OCT is shown below.
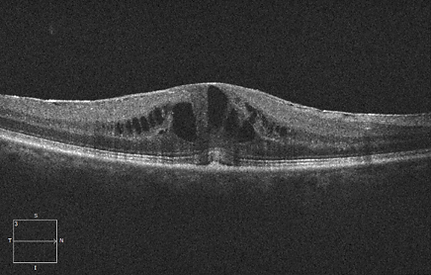
Question: What abnormalities do you visualize in the patient's OCT image?
What is the Diagnosis?

Question: Which of the following is the most reasonable first-line therapy for the patient's diagnosis?
Learning Objectives:
1) Identify OCT findings associated with CME.
2) Recognize the first line therapy for post-operative CME.
bottom of page
.png)